Department of Computational and Data Sciences
Scalable Systems for Data Science
- Instructors: Yogesh Simmhan (email) (www)
- TA: Pranjal Naman (email), TBD
- Course number: DS256
- Credits: 3:1
- Semester: Jan 2025
- Lecture: Tue-Thu 330-5pm (First class on Tue 13 Jan, 2026), Tutorials: TBD
- Room: CDS 202
- Teams: Teams Link (Join using Teams Code v0xq5zv)
- Pre-requisites: Data Structures, Programming and Algorithm concepts. Programming experience required. Basic knowledge of Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
- See 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, 2025 webpages
Overview
This course will teach the fundamental “systems” aspects of designing and using scalable data science platforms. Such platforms are used to store, manage, pre-process and train ML models over datasets that are large, fast and linked. In particular, we will examine the data engineering pipelines required to prepare data before DNN and LLM training. We will also explore scalable machine learning methods using distributed and federated approaches, besides Big Data platforms used to scale enterprise data.
There are two key changes this term:
- Besides examining the architectural design of several contemporary data platforms: Google’s GFS/Apache HDFS, Apache Spark (RDD/DF/ML/Streaming), PyTorch Distributed, Amazon’s DynamoDB/Apache Cassandra, Apache Kafka and Google’s Pregel/Apache Giraph, this term we will also be examining Design Pattern for Distributed Systems used by these systems to achieve scalability, throughput, reliability, etc.
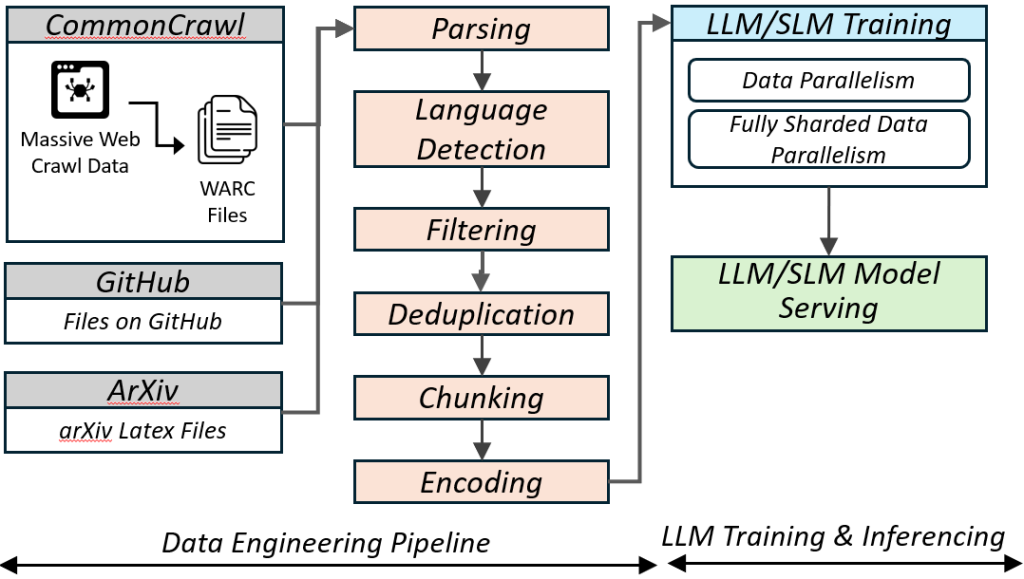
- Instead of a self-selected team project, the entire class will do a semester-long project on designing a pre-processing pipeline for training an LLM (SLM) using Apache Spark, and subsequently performing distributed model training using Pytorch Distributed and serving the model.
The course modules will cover all layers of a scalable data science and scalable ML stack:
- How do you store and query data at scale, using distributed file systems such as GFS/HDFS and Ceph and using cloud/NoSQL databases such as HBase and Dynamo?
- How do you pre-process data at large volumes in preparation for machine learning using distributed processing systems on the cloud, such as Apache Spark?
- How do you perform scalable training for both classic and deep learning using distributed training patterns and platforms such as parameter server, model/pipeline parallelism, federated learning, SparkML, Pytorch Distributed and DistDGL? How do we serve model inferencing at scale on distributed systems, including LLMs and GNNs?
- How do you process fast and linked data for applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) and fintech using platforms such as Kafka, Spark Streaming and Giraph?
There will also be guest lectures by experts from the industry and academia who work on Data Science platforms and machine learning applications in the real-world.
The course will have one common hands-on course project for 35 points performed in teams of 2-4 (TBD) split into 3 parts: (1) Pre-processing pipeline for LLM (SLM) training, (2) Distributed training of LLM (SLM), and (3) Scalable inferencing of LLM (SLM), with a bulk of the weightage for #1 and reducing for #2 and #3.
There will also be one literature review and paper presentation (10 points).
Lastly, there will be 2 midterm quizzes (2×15 points) and a final exam (25 points) in in-class proctored to form the rest of the grading.
Pre-requisites
This is an introductory course on the design of platforms for data engineering analytics over Big Data. However, you need prior knowledge on basics of computer systems, data structures, algorithms and good programming skills (preferably in Python). You will also need basic knowledge of Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Tentative Schedule
- First class on Tue 13 Jan at 330PM at CDS 202
- Introduction to Distributed Systems & Big Data Storage (Starts 13 Jan, ~4 lectures)
- Intro to Big Data
- Contrast Big Data systems: HBase/Big Table, Cassandra/Key-Value Store, Graph DB overview
- Understand the role of distributed systems. Understand distinction between weak and strong scaling.
- Distributed File Systems/HDFS/GFS/Ceph
- Cloud storage
- Required Reading
- Scalable problems and memory-bounded speedup, Sun and Ni, JPDC, 1993
- The Google File System, Sanjay Ghemawat Howard Gobioff Shun-Tak Leung, ACM SOSP, 2003
- Optional Reading
- Ceph: A scalable, high-performance distributed file system. Weil, Sage, et al. OSDI. 2006.
- Ceph: A scalable, high-performance distributed file system. Weil, Sage, et al. OSDI. 2006.
- Processing Large Volumes of Big Data (Starts ~27 Jan, ~5 lectures)
- Big Data Processing with MapReduce and Apache Spark
- Spark Basics, RDD, transformations, action, Shuffle
- Spark internals & Spark tuning
- Spark DataFrames, Spark SQL and Catalyst Optimizer
- Required Reading
- MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters, Dean and Ghemawat, USENIX OSDI, 2004
- Resilient distributed datasets: A fault-tolerant abstraction for in-memory cluster computing, Matei Zaharia, et al., USENIX NSDI, 2012
- Spark SQL: Relational Data Processing in Spark, Michael Armbrust, et al., ACM SIGMOD 2015
- Optional Reading
- Select chapters from Learning Spark, Holden Karau, et al., 1st Editions and Learning Spark, Jules S. Damji, Brooke Wenig, Tathagata Das, Denny Lee, 2nd Edition
- Clash of the Titans: MapReduce vs. Spark for Large Scale Data Analytics, JuweiShi, YunjieQiu, Umar Farooq Minhas, Limei Jiao Chen Wang, Berthold Reinwald, and Fatma Ozcan
- VLDB 2015
- The RefinedWeb Dataset for Falcon LLM, Guilherme Penedo, et al, NeurIPS 2023
- LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models, Hugo Touvron, et al., arXiv 2302.13971, 2023
- Tutorials (TBD)
- Quiz 1, Modules 1 and 2 (15 points) (12 Feb)
- Project Assignment #1 (20 points) (Posted on ~30 Jan, Due on ~27 Feb)
- Pre-processing pipeline for LLM(SLM) training using Apache Spark
- Pre-processing pipeline for LLM(SLM) training using Apache Spark
- Machine Learning at Scale (Starts ~17 Feb, ~5 lectures)
- ML over Big Data, Spark ML for ML pipelines.
- Data, Model and Pipeline parallelism. Parameter server. PyTorch Distributed.
- Training and Serving LLMs at scale
- Federated Learning platforms
- Scalable GNN training
- Reading
- Scaling Distributed Machine Learning with the Parameter Server, Li, Mu, et al., USENIX OSDI, 2014
- Towards federated learning at scale: System design, Bonawitz, Keith, et al., SysML Conference, 2019
- Beyond Data and Model Parallelism for Deep Neural Networks, Zhihao Jia, et al., MLSys 2019
- PyTorch distributed: experiences on accelerating data parallel training, Shen Li, et al, PVLDB, 2020
- Orca: A Distributed Serving System for Transformer-Based Generative Models, Gyeong-In Yu, et al., USENIX OSDI 2022
- Parallel and Distributed Graph Neural Networks: An In-Depth Concurrency Analysis, Besta and Hoefler, IEEE TPAMI, 2024
- Project Assignment #2 (10 points) (Posted on ~6 Mar, Due on ~20 Mar)
- Distributed training of LLM(SLM) training using Pytorch Distributed
- Distributed training of LLM(SLM) training using Pytorch Distributed
- NoSQL Databases (Starts ~10 Mar, ~4 lectures)
- Consistency models and CAP theorem/BASE
- Amazon Dynamo/Cassandra distributed key-value store
- Overview of HBase/Big Table, Graph Databases, Vector Databases
- Overview of Data Warehousing, Data Lakes, ETL, Cloud NoSQL
- Reading
- The dangers of replication and a solution, Jim Gray, Pat Helland, Patrick O’Neil, Dennis Shasha, ACM SIGMOD Record, 1996
- CAP Twelve Years Later: How the “Rules” Have Changed, Eric Brewer, IEEE Computer, 2012
- Dynamo: amazon’s highly available key-value store, DeCandia G, Hastorun D, Jampani M, Kakulapati G, Lakshman A, Pilchin A, Sivasubramanian S, Vosshall P, Vogels W. ACM SOSP, 2007
- Select chapters from Learning Spark, Jules S. Damji, Brooke Wenig, Tathagata Das, Denny Lee, 2nd Edition
- Quiz 2, Modules 3 and 4 (15 points) (24 Mar)
- Project Assignment #3 (5 points) (Posted on ~27 Mar, Due on ~10 Apr)
- Scalable LLM Serving
- Selection of Research Paper for Presentation (Due ~25 Mar)
- Processing Fast Data & Linked Data (Starts ~26 Mar, ~4 lectures)
- Need for Fast Data Processing. Internet of Things (IoT) application domain.
- Difference between low-latency ingest, analytics and querying.
- Publish-subscribe systems and Apache Kafka
- Streaming dataflows: Spark Streaming, Twitter Heron, Apache Flink
- Distributed graph processing, Vertex Centric Programming, Pregel, Giraph algorithms
- Reading
- Kafka: A Distributed Messaging System for Log Processing, Jay Kreps, Neha Narkhede, Jun Rao, NetDB, 2011
- DSTREAM
- Pregel: a system for large-scale graph processing, Malewicz, et al, ACM SIGMOD 2010
- Guest Lectures
- Talks by industry speakers throughout the semester and end of semester
- Research Reading and Presentations (10 points) (~Fri 17 Apr)
- Presenting one research paper
- Peer review
- Final Exam (25 points)(TBD)
Papers for Presentation
Some papers to choose that can be used for presentation are given below. Students can also propose alternative papers and get them approved.
- TBD
Assessments and Grading
|
Weightage |
Assessment |
|---|---|
|
35% |
One hands-on programming course project on pre-processing pipeline, training and inferencing for LLMs (20%+10%+5%) |
|
30% |
2 Midterm Quizzes (15%+15%) |
|
10% |
Paper Presentation at end of term |
|
25% |
Final exam |
Teaching & Office Hours
- Lecture: Tue and Thu, 330-5pm
- Classroom: CDS 202
- Office Hours: By appointment
Resources
- Patterns of Distributed Systems, Unmesh Joshi, Martin Fowler, 2023
- Online Teams Channel (Use Teams Code: v0xq5zv)
- Cluster Access: Students will validate their assignments and projects on the CDS
turingcluster and Cloud resources. Details for accessing the cluster and running programs on it will be covered in a lab session.
Academic Integrity
Students must uphold IISc’s Academic Integrity guidelines. We have a zero-tolerance policy for cheating and unethical behavior in this course. Use of Generative AI (ChatGPT, Copilot, etc.) in completing any of the assessments, including project coding/reports and presentation, is not permitted. Failure to follow these guidelines will lead to sanctions and penalties.
Learning takes place both within and outside the class. Hence, discussions between students, reference to online material and conversations with chatbots is encouraged as part of the course to achieve the intended learning objectives. However, while you may learn from any valid source, you must form your own ideas and complete problems and assignments by yourself. All works submitted by the student as part of their academic assessment must be their own.




